Post-money valuation refers to the value of a company after a funding round is completed. It takes into account the amount of funding that has been raised, as well as any changes in the company’s valuation since the last funding round.
Understanding post-money valuation is crucial for companies that are looking to raise external funding, as it helps them to set realistic valuations for future funding rounds and to make informed decisions about new funding opportunities. Additionally, post-money valuation is often used as a benchmark to measure a company’s growth and success. By understanding post-money valuation, companies can make informed decisions about how to raise the necessary capital to support their growth and development.
Pre-Money vs Post-Money Valuation
Pre-money valuation refers to the value of a company before a funding round is completed, whereas post-money valuation is the value of the company after a funding round is completed.
The main difference between pre-money and post-money valuation is the inclusion of external funding in the post-money valuation. The pre-money valuation only takes into account the company’s existing assets and operations, while the post-money valuation also includes the funds that were raised during the funding round.
Understanding the distinction between pre-money and post-money valuation is important because it can affect how a company is valued in future funding rounds. For example, if a company has a high pre-money valuation but a low post-money valuation, it may be difficult for them to secure funding in future rounds. Additionally, pre-money valuations are used to establish valuation caps for the company, which limits the amount of money that can be raised in the funding round. Pre and post money valuations matter in fundraising and investment because it helps stakeholders to understand the true value of the company and make informed decisions about investing in the company.
Calculating Post-Money Valuation
Calculating post-money valuation is the process of determining the value of a company after a funding round. The post-money valuation is calculated by adding the total amount of external funding raised during the funding round to the company’s pre-money valuation.
Factors that can affect post-money valuation include the company’s revenue and earnings, the size of the funding round, the number of shares issued, the share price, and the fully diluted capitalization.
Common methods used to calculate post-money valuation
Common methods used to calculate post-money valuation include the discounted cash flow method, the comparable company analysis method, and the precedent transaction method. The choice of method will depend on the company’s stage of development, the type of equity financing being raised, and the availability of comparable financial data. It is also important to note that post-money valuation can also be affected by the ownership stake of the investors and the terms of the investment.
How to Calculate Post-Money Valuation
Step-by-step guide on how to calculate post-money valuation
- Determine the pre-money valuation of the company before the investment round.
- Add the total amount of external funding raised during the investment round to the pre-money valuation.
- The result is the post-money valuation.
Tips and best practices for calculating post-money valuation
- Always use the most recent financial data when calculating post-money valuation.
- Be transparent and consistent with the method used to calculate post-money valuation.
- Consider the stage of development and size of the company when choosing a valuation method.
- Take into account the investment amount and the ownership stake that will be acquired for a given investment.
- Keep in mind that post-money valuation can change with future funding rounds, so it should be regularly updated.
- Seek advice from investment professionals and experts to ensure that the post-money valuation is accurate and fair.
Note: The above steps might vary depending on the company’s stage of development, the type of equity financing being raised, and the availability of comparable financial data. It’s always best to consult with investment professionals, financial experts, and legal advisors to ensure that the post-money valuation is accurate and fair.
Post-Money Valuation Formula
Explanation of the formula used to calculate post-money valuation: The formula to calculate post-money valuation is: Post-Money Valuation = Pre-Money Valuation + External Funding. This formula takes into account the company’s pre-existing value (pre-money valuation) and the external funding that has been raised during the current funding round.
How to use the post-money valuation formula to calculate the post-money valuation: The formula can be used by simply adding the pre-money valuation and external funding together.
Here is an example using sample data in a spreadsheet:
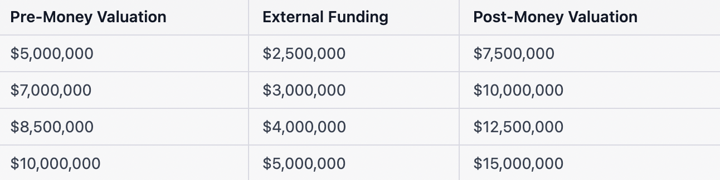
In the first column, the pre-money valuation of the company before the investment round is entered. In the second column, the total amount of external funding raised during the investment round is entered. In the final column, the pre-money valuation and the external funding are added to get the post-money value.
It is important to note that the post-money valuation will change with future funding rounds, so it should be regularly updated to reflect the current post-money value. This formula can be used by the companies and potential investors, venture capitalists or even early stage companies to evaluate the value of the company before and after a funding round.
Calculating Pre-Money Valuation
Step-by-step guide on how to calculate pre-money valuation
- Determine the company’s current financials, such as revenue, earnings, and assets.
- Use a valuation method such as discounted cash flow analysis or comparable company analysis to estimate the company’s future financials and performance.
- Use the information from steps 1 and 2 to calculate the pre-money valuation of the company.
Tips and best practices for calculating pre-money valuation
- Always use the most recent financial data when calculating pre-money valuation.
- Be transparent and consistent with the method used to calculate pre-money valuation.
- Consider the stage of development and size of the company when choosing a valuation method.
- Keep in mind that pre-money valuation can change with future funding rounds, so it should be regularly updated.
- Seek advice from investment professionals and experts to ensure that the pre-money valuation is accurate and fair.
Here is an example pre-money valuation:
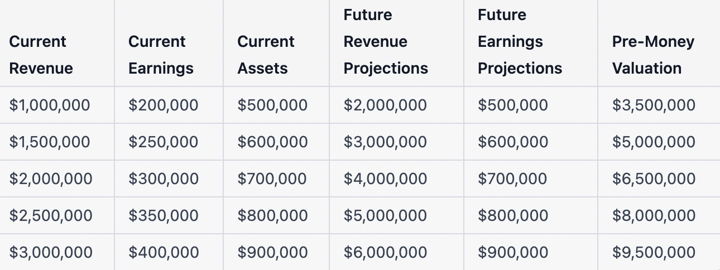
In this example, the current revenue, earnings, and assets of the company are entered in the first three columns. The next two columns show the future revenue and earnings projections, which are used to estimate the company’s future financials and performance. The final column is where the pre-money valuation is calculated by using the information from the previous columns and a chosen valuation method.
Please note that the above spreadsheet is just an example and the actual numbers would depend on the company’s financials, projections and investment terms and conditions. It’s important to understand pre-money value and use accurate and fair data to calculate pre-money valuations to make sure that the company is fairly valued for potential investors, venture capitalists or even early stage companies.
Pre-Post Money Valuation
Explanation of pre-post money valuation
Pre-post money valuation refers to the value of a company both before and after a funding round. It includes both the pre-money valuation and the post-money valuation. The pre-money valuation represents the value of a company before an investment round, while the post-money valuation represents the value of a company after an investment round.
How pre-post money valuation is used in fundraising and investment
Pre-post money valuation is used in fundraising and investment to provide a complete picture of a company’s value over time. It helps companies to understand their growth and progress, and it helps investors to understand the potential returns on their investment. It also serves as a benchmark for measuring a company’s success. Additionally, pre-post money valuation can be used to compare different companies or different rounds of funding, and it can be used to negotiate fair valuations and investment terms.
It’s important to note that pre-post money valuation should be regularly updated to reflect the current value of the company, and it should be used in conjunction with other financial metrics to provide a comprehensive understanding of a company’s financial health.
Pre and Post Money Valuation Example
- An example of how to calculate pre and post-money valuation:
- Determine the company’s pre-money valuation, in Uber’s case it was $68 billion
- Determine the amount of external funding raised, in Uber’s case it was $3.5 billion
- Add the pre-money valuation and external funding to calculate the post-money valuation. In this case, $68 billion + $3.5 billion = $71.5 billion.
Here is an example pre and post-money valuation:

This is an example of how to calculate pre and post-money valuation and it’s based on real-world data of the company Uber. It’s important to note that this is a snapshot of a specific funding round and valuations can change over time.
Summary of key takeaways on post-money valuation and its importance in fundraising and investment
Understanding post-money valuation is crucial for companies and investors to make informed decisions about fundraising and investment opportunities. It will give insight into the potential returns on investment and the ownership stake that will be acquired for a given investment amount. Additionally, it is important to understand the distinction between pre-money and post-money valuation, and how they interact. The relationship between pre-money and post-money valuation is key to evaluate a company’s value over time.
Additional resources for further learning on post-money valuation:
- The Venture Capital Method for Valuation by Bill Aulet
- The Art of Startup Fundraising by Alejandro Cremades
- Mastering the VC Game: A Venture Capital Insider Reveals How to Get from Start-up to IPO on Your Terms by Jeffrey Bussgang
- Venture Capital and the Finance of Innovation by Christopher G.
- Kauffman Foundations
- National Venture Capital Association (NVCA)
- Seedrs Academy
These resources provide a deeper understanding of post-money valuation and its importance in fundraising and investment, as well as additional information on pre-money valuation, fundraising strategies and the venture capital industry.




